TB-MBLA
A potential test for both diagnosis and monitoring of TB over time.
For the last five years, LifeArc has been partnered with the University of St Andrews in developing the TB-MBLA – ‘Tuberculosis Molecular Bacterial Load Assay.’
TB-MBLA kits utilise RT-qPCR to estimate viable TB bacterial load in patient sputum samples. This ability to detect viable bacteria means the kit can be used to monitor a patient’s response to anti-TB therapy over time.
Overview
In 2021, an estimated 10.6 million people developed active TB, resulting in 1.6 million deaths*. There are currently limited options for monitoring the disease, but for the last five years, LifeArc has been working with collaborators from the University of St Andrews on developing the TB-MBLA – a test that could be used for both diagnosis and monitoring of TB over time.
The assay targets 16S rRNA from actively growing TB cells, which has been shown to be a more reliable indicator of active infection than DNA targets. In addition, with results available in a few hours, TB-MBLA has significantly shorter time to result compared with methods such as TB culture.
How is the TB-MBLA test being used?
LifeArc has now configured the assay as an RT-qPCR kit suitable for research use only.
The kit is currently being assessed in the TIME study (TB DIagnosis and Monitoring Evaluation) which is running in four clinical sites across Tanzania and Uganda until the end of 2024. The aim of the study is to evaluate how accurate the assay is at detecting TB in sputum samples from participants with pulmonary TB, compared with a number of other established diagnostic methods currently used in TB clinical care around the world.
*WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2022
Want to know more?
Get in touch with the team using the form below.
Contact us
In submitting your personal data via this form, you consent to being contacted via the details provided so that your enquiry can be responded to. If you would like your data to be removed, please email dataprivacy@lifearc.org.
Please see our Privacy Policy in relation to the personal data you submit to us through this page.
Latest news
-
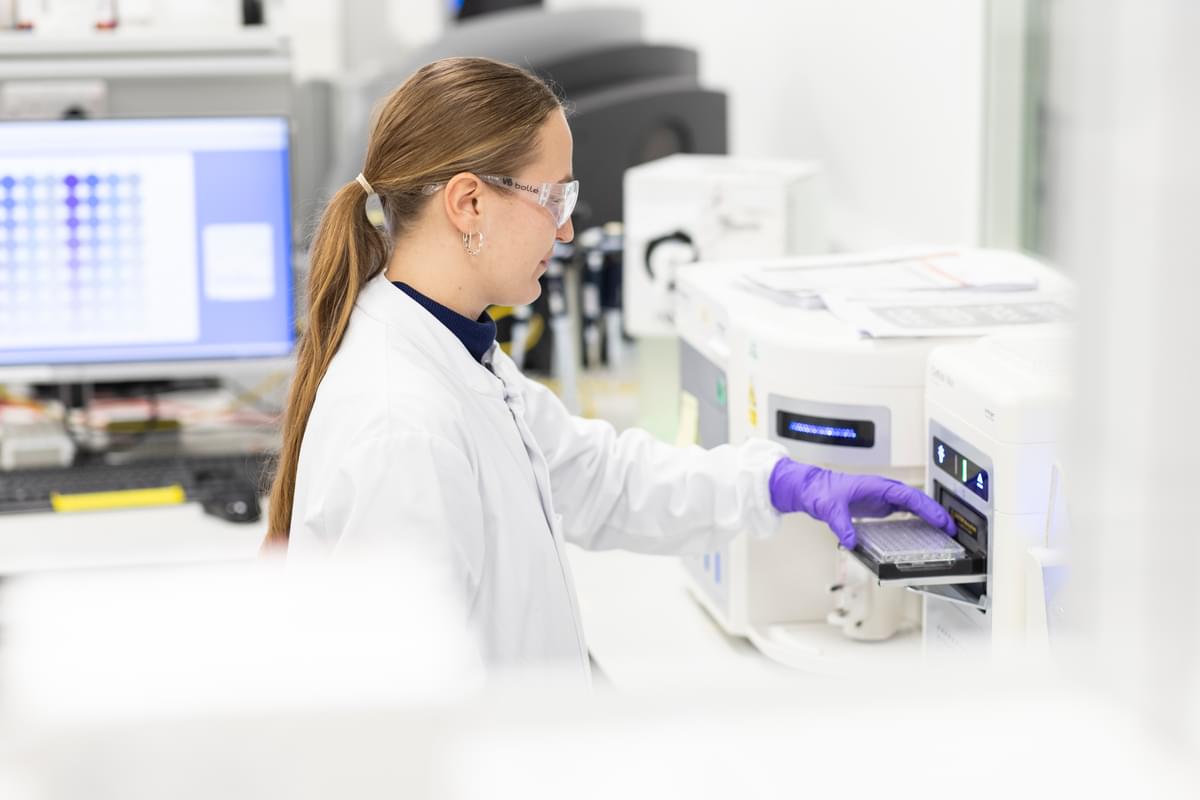

First-of-a-kind plan announced to get more children access to cutting-edge, proven gene therapy treatments for rare diseases
Read more: First-of-a-kind plan announced to get more children access to cutting-edge, proven gene therapy treatments for rare diseases -
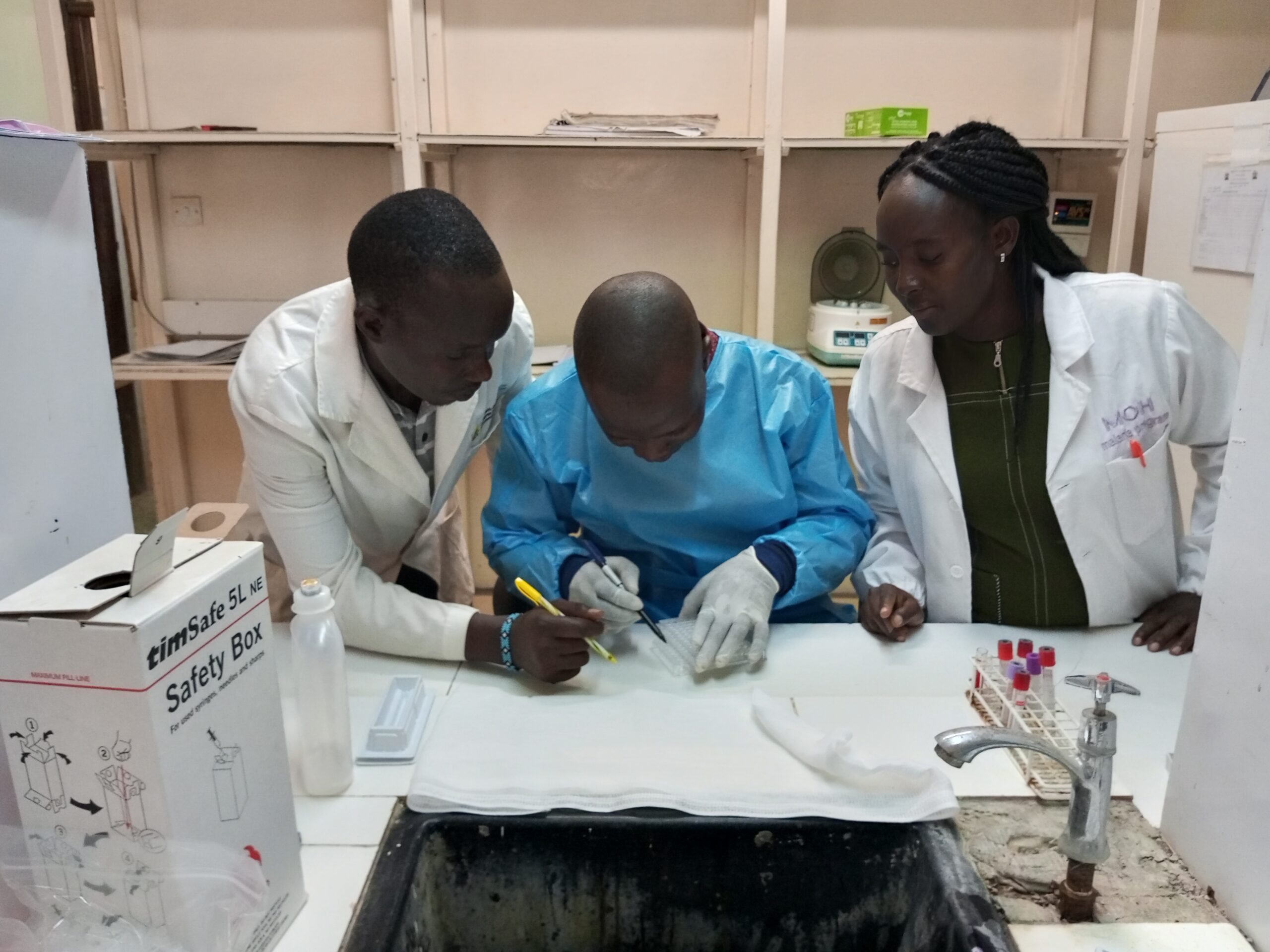

New £6.2m partnership will help to eliminate a deadly disease affecting children and vulnerable people in Kenya
Read more: New £6.2m partnership will help to eliminate a deadly disease affecting children and vulnerable people in Kenya -

LifeArc supports 8 new fellows through Crick Africa Network (CAN) partnership
Read more: LifeArc supports 8 new fellows through Crick Africa Network (CAN) partnership
